For individuals managing Type 2 diabetes, certain supplements are frequently explored for their potential to support blood sugar control and overall health when used alongside conventional treatment. Key options often discussed include Berberine, Alpha-Lipoic Acid, Chromium, Magnesium, and Vitamin D, each offering unique mechanisms that may contribute to better glycemic management or address common deficiencies. It is paramount, however, to consult with your healthcare provider before introducing any new supplement into your routine to ensure safety and avoid interactions with existing medications.
Understanding Supplements in Type 2 Diabetes Management

Navigating the landscape of Type 2 diabetes management involves a multi-faceted approach, and while supplements can play a supportive role, it’s crucial to understand their place within your overall health strategy. Think of them as helpful teammates, not star players that can win the game alone.
* Adjunct, Not Replacement: It’s absolutely vital to remember that supplements are meant to complement, not replace, your prescribed medications, a balanced, whole-food diet, and regular physical activity. These foundational pillars remain the cornerstones of effective diabetes management. Relying solely on supplements or using them to justify neglecting medical advice or lifestyle changes can be dangerous and counterproductive. They offer an additional layer of support, working in harmony with your established routine.
* Individualized Needs: Diabetes is a highly personal journey, and what works wonderfully for one person might not be suitable or effective for another. The effectiveness and safety of supplements can vary greatly depending on an individual’s specific health status, existing conditions (like kidney disease or heart issues), other medications they are taking, and even their genetic makeup. A personalized approach, carefully guided by your healthcare team, is the safest and most effective path to exploring supplement options.
* Evidence-Based Approach: The supplement market can feel like a Wild West, filled with grand claims and enticing promises. To make informed choices, focus on supplements with a reasonable and robust body of scientific evidence supporting their use, rather than anecdotal claims, internet hearsay, or aggressive marketing. Look for clinical trials, meta-analyses, and recommendations from reputable health organizations. Always be skeptical of products that promise a “cure” or sound too good to be true. Your doctor or a registered dietitian can help you sift through the noise and identify genuinely promising options.
Chromium Picolinate for Glucose Metabolism
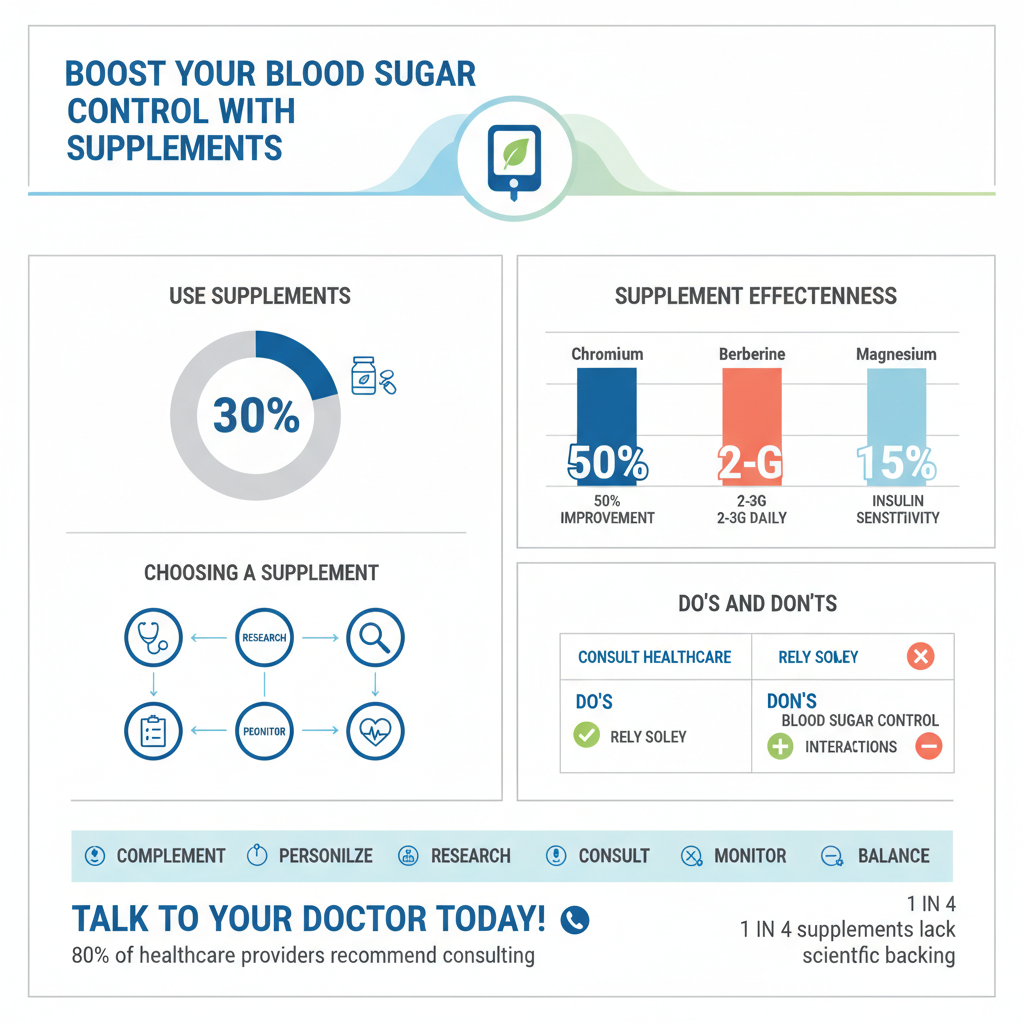

Chromium is a fascinating trace mineral that’s essential for several bodily functions, particularly those related to how your body processes nutrients. For individuals with Type 2 diabetes, it’s often considered for its potential role in optimizing glucose metabolism.
* Insulin Sensitivity: At its core, chromium plays a crucial role in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. It’s thought to enhance the action of insulin, which is the hormone responsible for ushering glucose from your bloodstream into your cells for energy. Think of insulin as a key that unlocks your cells, and chromium as something that helps that key fit better in the lock. By potentially improving insulin’s efficiency, chromium can help your cells absorb glucose more effectively, leading to lower blood sugar levels. It’s part of a molecule called chromodulin, which is believed to potentiate insulin signaling.
* Forms and Dosage: While various forms of chromium exist, chromium picolinate is the most common and well-absorbed form found in supplements. This form combines chromium with picolinic acid, which is believed to enhance its bioavailability. Typical dosages explored in studies for blood sugar management range from 200-1000 mcg (micrograms) per day. However, determining the right dosage for you should always be done in consultation with your medical professional, as individual needs and existing conditions can influence the appropriate amount. It’s not a “more is always better” situation.
* Considerations: Research on chromium’s benefits for Type 2 diabetes has shown mixed results, with some studies suggesting it may slightly reduce fasting blood glucose and HbA1c (a measure of average blood sugar over 2-3 months) in some individuals, particularly those with a deficiency. The benefits are often modest, so it’s important to have realistic expectations. It’s generally considered safe at recommended doses, but potential interactions should be noted. For instance, chromium supplements may interact with thyroid medications, potentially affecting their absorption or efficacy, so timing of doses might be important. Always disclose all supplements to your doctor, especially if you’re on multiple medications.
Berberine: A Potent Plant Alkaloid

Berberine is a bioactive compound extracted from several different plants, including the Berberis genus, goldenseal, and Oregon grape. It has a long history of use in traditional Chinese medicine and is gaining significant attention in modern research for its wide-ranging metabolic benefits.
* Mechanism of Action: What makes berberine so intriguing is its complex and multifaceted mechanism of action, which remarkably parallels that of some common diabetes medications. One of its primary ways of working is by activating AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase), an enzyme often referred to as a “master switch” for metabolism. By activating AMPK, berberine can improve insulin sensitivity, meaning your body’s cells respond better to insulin. It also helps reduce glucose production in the liver (gluconeogenesis), preventing the liver from releasing too much sugar into the bloodstream. Furthermore, berberine can slow the breakdown of carbohydrates in the gut, leading to a more gradual absorption of glucose. These combined actions offer a powerful approach to glycemic control.
* Blood Sugar & Lipid Benefits: A growing body of scientific evidence suggests that berberine can significantly lower various markers of blood sugar control. Studies have shown impressive reductions in fasting blood glucose, post-meal blood glucose, and HbA1c levels, often comparable to conventional medications. But its benefits don’t stop there! Berberine has also been shown to improve lipid profiles, leading to reductions in “bad” LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, which are often elevated in individuals with Type 2 diabetes and increase cardiovascular risk.
* Side Effects: While highly effective, berberine can come with some common side effects, primarily related to gastrointestinal upset. These can include diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, and nausea, especially when first starting or at higher doses. To minimize these, it’s generally recommended to start with a low dose (e.g., 500 mg once or twice daily) and gradually increase it as tolerated, preferably taken with meals. Because of its potency and potential for drug interactions (e.g., with blood thinners or liver-metabolized drugs), it is absolutely critical to use berberine only under the guidance of your healthcare provider.
Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA) for Neuropathy Support
Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA) is a naturally occurring compound that functions as a powerful antioxidant in the body. It’s unique because it’s both fat-soluble and water-soluble, allowing it to work in virtually every cell and tissue, making it a versatile player in health support.
* Antioxidant Power: In Type 2 diabetes, chronic high blood sugar levels can lead to increased oxidative stress – a damaging process caused by an imbalance between free radicals and the body’s ability to neutralize them. This oxidative stress can harm cells, tissues, and particularly nerves. ALA steps in as a potent antioxidant, helping to neutralize these harmful free radicals, thereby protecting cells from damage. What’s even more impressive is that ALA can also regenerate other important antioxidants in the body, such as vitamins C and E, and glutathione, further amplifying its protective effects against oxidative damage.
* Diabetic Neuropathy: This is arguably where ALA shines brightest for individuals with Type 2 diabetes. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy, characterized by nerve damage that often causes pain, burning, tingling, or numbness in the hands and feet, is a common and debilitating complication of diabetes. Research, particularly in Europe, has extensively studied ALA for its potential to alleviate these symptoms. It’s believed to work by improving blood flow to nerves, reducing oxidative stress directly on nerve cells, and enhancing nerve function. For many, ALA can provide significant relief from the discomfort and progression of neuropathy.
* Dosage and Forms: For the management of diabetic neuropathy symptoms, typical dosages of Alpha-Lipoic Acid often range from 600-1200 mg per day. These doses are usually split and taken throughout the day. When choosing an ALA supplement, you might encounter different forms. The “R-lipoic acid” form is considered the naturally occurring and more bioavailable form that your body can utilize more effectively. The “S-lipoic acid” form is synthetic and less active. Many supplements contain a racemic mixture of both R and S forms (often simply labeled “Alpha-Lipoic Acid”). Opting for products that specify R-lipoic acid might offer enhanced efficacy, although both forms have shown benefits. As with all supplements, discussing the appropriate form and dosage with your doctor is essential, especially given its potential to lower blood sugar and interact with other medications.
Magnesium and Vitamin D: Essential Micronutrients
Magnesium and Vitamin D are two micronutrients that are absolutely critical for overall health, and their importance is particularly highlighted in the context of Type 2 diabetes due to widespread deficiencies and their profound impact on metabolic function.
* Magnesium’s Role: It might surprise you just how vital magnesium is – it’s a cofactor in over 300 enzymatic reactions in the body! These reactions include those essential for energy production, nerve function, muscle contraction, and crucially, glucose metabolism and insulin signaling. Many individuals with Type 2 diabetes are found to be deficient in magnesium, often due to increased urinary excretion of the mineral caused by high blood sugar. Low magnesium levels can worsen insulin resistance, as magnesium is required for insulin receptors to function correctly and for the proper utilization of glucose. Supplementation, particularly in deficient individuals, may improve insulin sensitivity, helping the body respond more effectively to insulin and manage blood sugar levels.
* Vitamin D Deficiency: Similar to magnesium, low Vitamin D levels are incredibly common worldwide, and a significant portion of people with Type 2 diabetes are deficient. This “sunshine vitamin” acts more like a hormone in the body and plays a role in numerous processes, including immune function and bone health. Importantly for diabetes, low Vitamin D levels have been linked to impaired insulin secretion from the pancreatic beta cells and increased insulin resistance in peripheral tissues. Ensuring adequate Vitamin D levels, especially through supplementation in deficient individuals, may offer benefits by improving beta-cell function and enhancing insulin sensitivity, contributing to better glycemic control.
* Testing is Key: Because deficiencies in both magnesium and Vitamin D are prevalent and their levels can be influenced by various factors, it’s highly advisable to have your levels tested before embarking on supplementation. A simple blood test can reveal your current status for serum magnesium and 25-hydroxyvitamin D. This information allows your healthcare provider to recommend the most appropriate dosage, ensuring you’re not taking too much or too little, and that supplementation is truly targeted to address a specific deficiency rather than simply guessing. This personalized approach maximizes safety and potential benefits.
Critical Considerations Before Supplementing
While the potential benefits of certain supplements for Type 2 diabetes can be exciting, it’s imperative to approach supplementation with caution and a well-informed strategy. Your safety and overall health always come first.
* Healthcare Professional Consultation: This cannot be stressed enough: always, always discuss any supplement plans with your doctor, endocrinologist, or a registered dietitian. They have a comprehensive understanding of your medical history, current medications, and specific health needs. They can assess whether a particular supplement is safe and appropriate for you, help you understand potential risks versus benefits, and monitor your progress. Never start a new supplement without their explicit approval, especially when managing a complex condition like Type 2 diabetes.
* Potential Drug Interactions: This is one of the most significant reasons for medical consultation. Supplements, even “natural” ones, are biologically active and can interact with prescribed medications, leading to adverse effects or altering the efficacy of your drugs. For instance:
* Berberine can significantly lower blood sugar, potentially causing hypoglycemia if combined with insulin or oral hypoglycemic medications. It can also interfere with liver enzymes responsible for metabolizing many drugs, including blood thinners, statins, and certain antidepressants.
* Chromium may interact with thyroid medications, antacids, or NSAIDs.
* Alpha-Lipoic Acid can also lower blood sugar and potentially interact with chemotherapy drugs.
* Magnesium can affect the absorption of certain antibiotics, diuretics, and blood pressure medications.
* Vitamin D can interact with corticosteroids, weight-loss drugs like orlistat, and certain statins.
Such interactions can be dangerous, making your medications either too strong or too weak.
* Quality and Purity: The supplement industry is not as tightly regulated as the pharmaceutical industry, meaning product quality can vary wildly. It’s crucial to choose high-quality supplements from reputable brands that prioritize third-party testing. Look for seals of approval from organizations like NSF International, USP (U.S. Pharmacopeia), or ConsumerLab.com. These certifications indicate that the product has been independently tested to ensure it contains what it claims, in the amounts specified, and is free from harmful contaminants like heavy metals, pesticides, or undeclared ingredients. Avoiding proprietary blends where ingredient amounts aren’t fully disclosed is also a good practice.
* Monitor and Track: If, after consulting with your healthcare provider, you decide to incorporate a new supplement, diligent monitoring is key. Consistently track your blood glucose levels (and possibly blood pressure or other relevant metrics) to observe any changes. Keep a detailed log of the supplement, dosage, and any side effects you might experience, no matter how minor. Report all of this information to your healthcare provider during your follow-up appointments. This ongoing communication ensures that the supplement is working as intended, isn’t causing harm, and that your overall diabetes management plan remains optimized.
Navigating the world of supplements for Type 2 diabetes can be complex, but research highlights key players like Berberine, Alpha-Lipoic Acid, Chromium, Magnesium, and Vitamin D as potentially beneficial adjuncts to a comprehensive management plan. Remember that consistent lifestyle choices, prescribed medications, and regular monitoring remain the cornerstones of diabetes care. Before making any changes, empower yourself with knowledge and always prioritize a thorough discussion with your doctor to ensure that any supplements you consider are safe, appropriate, and truly contribute to your long-term health goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which supplements are most commonly recommended for individuals managing Type 2 diabetes?
Several supplements are frequently discussed for their potential benefits in managing Type 2 diabetes, including chromium, berberine, alpha-lipoic acid (ALA), and magnesium. These have shown promise in various studies for supporting blood sugar control, improving insulin sensitivity, and reducing oxidative stress. However, it’s crucial to remember that supplements should complement, not replace, prescribed medications and a healthy lifestyle.
Why is berberine often suggested for individuals with Type 2 diabetes?
Berberine is frequently suggested because research indicates it may help improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, effectively assisting the body in using insulin more efficiently. It’s thought to activate an enzyme called AMPK, which plays a key role in energy regulation and can help reduce glucose production in the liver and improve glucose uptake by cells. Many compare its mechanism of action to that of metformin, a common diabetes medication.
How can omega-3 fatty acids benefit someone managing Type 2 diabetes?
Omega-3 fatty acids, commonly found in fish oil, primarily benefit individuals with Type 2 diabetes by reducing chronic inflammation and supporting cardiovascular health, which is vital as diabetics have an increased risk of heart disease. While they don’t directly lower blood sugar, omega-3s can help improve triglyceride levels and overall heart function, indirectly contributing to better metabolic health. Always discuss appropriate dosing with a healthcare professional.
What important vitamins or minerals might Type 2 diabetics commonly be deficient in?
Individuals with Type 2 diabetes are often found to have deficiencies in certain vital nutrients, which can impact their overall health and diabetes management. Common deficiencies include Vitamin D, crucial for immune function and potentially insulin sensitivity; Magnesium, involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions including glucose metabolism; and Vitamin B12, especially for those taking metformin, as the medication can interfere with its absorption. Addressing these deficiencies through diet or supplementation, under medical guidance, can be beneficial.
Are there any specific supplements Type 2 diabetics should avoid, or precautions they should take?
Yes, Type 2 diabetics should exercise caution with many supplements and always consult their doctor before starting any new regimen, as some can interact negatively with medications or exacerbate conditions. Supplements that significantly lower blood sugar could cause hypoglycemia when combined with diabetes drugs, while others might interact with blood thinners or impact kidney function. It’s also important to avoid products with added sugars or unverified health claims, prioritizing safety and professional medical advice.
References
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/type-2-diabetes/in-depth/diabetes-supplements/art-20046546
- https://diabetes.org/healthy-living/medication-treatments/diet-nutrition-and-physical-activity/complementary-and-alternative-medicine
- Diabetes and Dietary Supplements: What You Need To Know | NCCIH
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/what-to-know-about-supplements-for-type-2-diabetes-202203102710
- https://health.clevelandclinic.org/are-there-any-supplements-that-can-help-with-diabetes/