For diabetics looking to lose weight, the most effective approach is typically a balanced, whole-foods diet that prioritizes lean protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates while carefully managing portion sizes and carbohydrate intake. This strategy not only aids in weight reduction but also helps stabilize blood sugar levels, reduce insulin resistance, improve overall metabolic health, and can significantly reduce the risk of diabetes complications. Embarking on this journey means adopting sustainable eating patterns that nourish your body, keep you energized, and support long-term well-being, moving beyond restrictive fads towards a truly healthy lifestyle. Below, we outline key principles and practical steps to guide you towards sustainable weight loss and better health.
The Foundation: Prioritizing Whole Foods and Portion Control

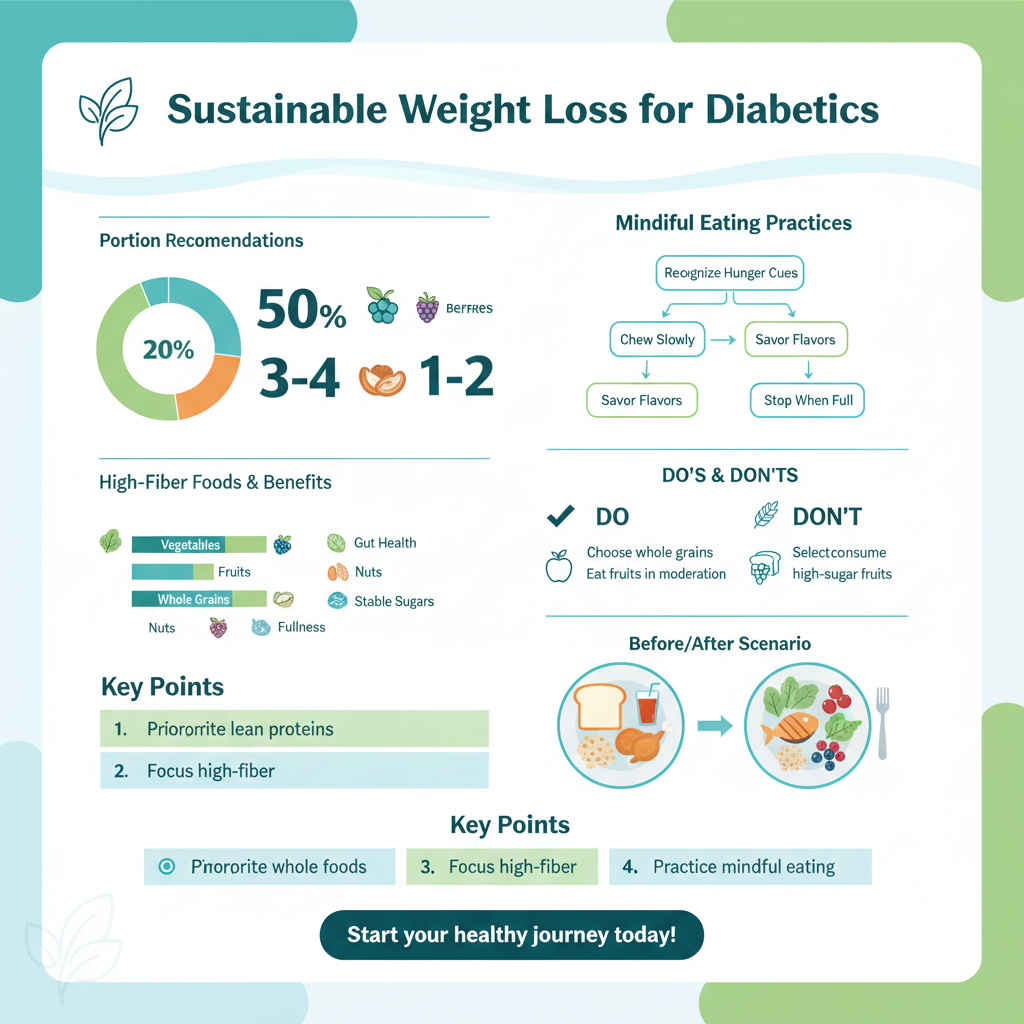
The cornerstone of any successful and healthy weight loss plan, especially for individuals managing diabetes, lies in building your diet around whole, unprocessed foods. These foods are packed with essential nutrients, fiber, and water, which are crucial for satiety, stable blood sugar, and overall metabolic function.
* Focus on unprocessed foods:
* Vegetables: Make non-starchy vegetables like leafy greens (spinach, kale), broccoli, cauliflower, bell peppers, zucchini, and cucumbers the bulk of your meals. They are very low in calories, high in fiber, and rich in vitamins and minerals, helping you feel full without spiking blood sugar. Aim to fill at least half your plate with these vibrant foods.
* Fruits: Enjoy fruits in moderation, focusing on berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries), apples, and pears, which are lower in sugar and higher in fiber than tropical fruits. Their fiber content helps to slow down sugar absorption.
* Lean Meats and Fish: Opt for skinless chicken breast, turkey, lean cuts of beef or pork, and a variety of fish, especially fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids beneficial for heart health and inflammation. These provide high-quality protein essential for muscle maintenance and satiety.
* Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, flax seeds, and sunflower seeds offer healthy fats, fiber, and some protein. They make excellent snacks in controlled portions, adding crunch and nutrients to your diet.
* Whole Grains: While managing carbohydrate intake, incorporating small portions of truly whole grains like quinoa, oats (steel-cut or rolled), brown rice, and farro can provide sustained energy and fiber.
* Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, and black beans are excellent sources of plant-based protein and fiber, making them filling and beneficial for blood sugar control.
* Practice mindful eating and pay attention to portion sizes: Mindful eating is about truly listening to your body’s hunger and fullness cues. Instead of just eating what’s on your plate, take your time, savor each bite, and notice how your body feels. Are you truly hungry, or just bored or stressed? This practice helps you recognize when you’ve had enough, preventing overeating. For portion control, remember that even healthy foods contribute calories. Using smaller plates, measuring your food initially to understand standard portion sizes (e.g., a deck of cards for protein, a cupped hand for nuts), and serving yourself appropriate amounts can make a huge difference in managing calorie intake without feeling deprived. It’s about being intentional with every mouthful.
* Eliminate or drastically reduce sugary drinks, processed snacks, and refined grains: These items are often laden with empty calories, added sugars, unhealthy fats, and refined carbohydrates, which are detrimental to weight loss and blood sugar management.
* Sugary drinks: Sodas, fruit juices (even 100% juice), sweetened teas, and coffee beverages cause rapid blood sugar spikes and contribute significantly to calorie intake without offering much satiety. Switch to water, unsweetened tea, or sparkling water with a squeeze of lemon.
* Processed snacks: Chips, cookies, cakes, and most packaged snack bars are engineered to be hyper-palatable, leading to overconsumption. They offer little nutritional value and can sabotage your weight loss efforts by encouraging cravings and unhealthy eating patterns.
* Refined grains: White bread, white rice, pasta made from refined flour, and many breakfast cereals are quickly broken down into sugar in your body, leading to blood sugar spikes and subsequent crashes that can fuel hunger and fatigue. Replacing these with their whole-grain counterparts or non-starchy vegetables is a game-changer.
Mastering Carbohydrate Choices

Carbohydrates are a major source of energy, but for diabetics, managing their type and quantity is paramount for both blood sugar control and weight loss. It’s not about cutting them out entirely, but rather making smarter, more informed choices.
* Choose complex carbohydrates from whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables: Complex carbohydrates, often referred to as “good” carbs, are rich in fiber and are digested slowly. This slow digestion prevents rapid spikes in blood sugar, providing a steady release of energy and helping you feel full for longer, which is crucial for weight management.
* Whole Grains: Beyond the examples given, consider steel-cut oats, quinoa, bulgur, farro, and 100% whole-wheat bread (in moderation). These offer sustained energy and essential nutrients.
* Legumes: Black beans, lentils, chickpeas, and kidney beans are powerhouse foods, providing both complex carbs and protein, along with a significant amount of dietary fiber.
* Non-starchy vegetables: As mentioned, these are your best friends. They are incredibly low in carbs but high in fiber and nutrients, allowing you to eat a large volume without significantly impacting blood sugar or calorie intake.
* Monitor carbohydrate intake and distribution throughout the day: This is a key strategy for managing diabetes and promoting weight loss. Instead of eating a large amount of carbohydrates at one meal, distribute them evenly across your meals and snacks. This helps your body process the carbohydrates more effectively, preventing large blood sugar fluctuations. Tools like food diaries, carb counting apps, or simply working with a dietitian can help you determine your individual carbohydrate needs. Your healthcare team can guide you on a target carbohydrate range per meal, typically starting around 30-45 grams for main meals, but this varies greatly per individual. Consistency in carb intake from day to day can also make blood sugar management much smoother.
* Understand the glycemic index and glycemic load of foods:
* Glycemic Index (GI): This ranks carbohydrates on a scale from 0 to 100 based on how quickly they raise blood sugar levels after eating. Foods with a high GI (like white bread, sugary cereals) cause rapid spikes, while low GI foods (like most vegetables, legumes, whole grains, and lean proteins) have a more gradual effect.
* Glycemic Load (GL): This provides a more realistic picture by taking into account both the GI and the actual amount of carbohydrate in a serving. A food might have a high GI but a low GL if its typical serving size contains very few carbohydrates (e.g., watermelon). Prioritizing foods with a low GL is generally recommended for diabetes management and weight loss, as they lead to smaller, slower rises in blood sugar. Familiarizing yourself with these concepts helps you make educated choices that support stable blood glucose and improve insulin sensitivity over time.
Leveraging Lean Protein and Healthy Fats

While managing carbohydrates is crucial, incorporating adequate amounts of lean protein and healthy fats is equally important for satiety, muscle preservation, and overall metabolic health, particularly when aiming for weight loss. These macronutrients have minimal impact on blood sugar and offer distinct benefits.
* Include adequate lean protein sources in every meal: Protein is a powerhouse for weight loss. It helps you feel fuller for longer, reducing the likelihood of overeating or snacking on unhealthy items. More importantly, protein helps preserve muscle mass, which is vital because muscle tissue burns more calories at rest than fat tissue. This means maintaining or building muscle helps boost your metabolism, making weight loss more efficient.
* Excellent sources include: Skinless chicken breast, turkey, fish (salmon, cod, tuna, sardines), eggs, Greek yogurt (plain, unsweetened), cottage cheese, tofu, tempeh, edamame, and a variety of lentils and beans.
* Practical tip: Aim for a palm-sized portion of lean protein at each main meal and consider protein-rich snacks like hard-boiled eggs or a handful of almonds between meals to keep hunger at bay.
* Incorporate healthy fats from avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil: Don’t fear fats – choose the right ones! Healthy fats are essential for hormone production, nutrient absorption (especially fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, K), and promoting satiety. Like protein, fats are digested slowly and don’t cause blood sugar spikes, contributing to stable energy levels.
* Sources of monounsaturated fats: Avocados, olive oil, and almonds are great choices.
* Sources of polyunsaturated fats (including omega-3s): Walnuts, flax seeds, chia seeds, fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), and certain vegetable oils like canola or soybean oil.
* Practical tip: Use olive oil for cooking and salad dressings, add a quarter of an avocado to your salad or sandwich, and snack on a small handful of nuts or seeds. Remember that fats are calorie-dense, so portion control remains important even for healthy fats.
* Protein and fats have minimal impact on blood sugar: This is a significant advantage for diabetics. When you build meals around protein and healthy fats, alongside your chosen complex carbohydrates, you create a balanced plate that helps slow down the absorption of glucose from the carbohydrates. This leads to a more gradual rise in blood sugar after meals, making it easier to manage your glucose levels and reduce insulin resistance. This stability is key not only for preventing diabetes complications but also for controlling hunger and reducing cravings, further supporting your weight loss goals.
Strategic Meal Planning and Hydration
Successful weight loss and diabetes management are rarely accidental. They require foresight and deliberate planning. Two simple yet powerful strategies are meal planning and consistent hydration.
* Plan meals and snacks in advance: This is perhaps one of the most effective habits you can adopt. When you plan your meals and snacks for the week, you take the guesswork out of eating, ensuring you have balanced, diabetes-friendly options readily available.
* Benefits: Reduces impulsive unhealthy food choices (no more reaching for fast food when you’re starving), helps control portion sizes, ensures variety in your diet, saves money, and most importantly, supports consistent blood sugar management and calorie control for weight loss.
* Practical tips: Dedicate some time each week (e.g., Sunday afternoon) to plan. Make a grocery list based on your plan. Consider “batch cooking” by preparing larger quantities of ingredients (like grilled chicken, roasted vegetables, or cooked quinoa) that can be mixed and matched throughout the week. Pack your lunch and snacks for work to avoid tempting cafeteria options or vending machines.
* Stay well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day: Water is essential for every bodily function, and it plays a crucial role in weight loss and diabetes management.
* Managing appetite: Often, our bodies confuse thirst with hunger. Drinking a glass of water before meals can help you feel fuller, leading to smaller food portions.
* Metabolism: Water is vital for metabolic processes, including the breakdown of fat. Staying hydrated ensures your metabolism functions optimally.
* Blood sugar: Adequate hydration helps your kidneys flush out excess sugar through urine, especially when blood sugar levels are high. It also prevents dehydration, which can sometimes make blood sugar levels appear higher.
* Practical tips: Carry a reusable water bottle with you and refill it throughout the day. Set reminders on your phone to drink water. Infuse your water with slices of lemon, cucumber, or berries for a refreshing, sugar-free flavor boost. Aim for at least 8 glasses (about 2 liters) of water daily, more if you’re active or in a hot climate.
* Consider meal timing and consistency: Establishing a regular eating schedule can significantly benefit blood sugar control and weight loss efforts.
* Regulate blood sugar: Eating at consistent times helps your body anticipate food intake and regulate insulin response more effectively. Skipping meals, especially breakfast, can lead to overeating later in the day and can cause erratic blood sugar fluctuations.
* Boost metabolism: Eating regular, balanced meals helps keep your metabolism humming. When you go too long without food, your body might slow down its metabolic rate to conserve energy.
* Reduce cravings: Consistent meal timing can help stabilize energy levels, preventing the drastic dips that often lead to strong cravings for sugary or high-carb foods. Aim for three balanced meals and 1-2 small, healthy snacks if needed, keeping similar time intervals between them.
Beyond Diet: Lifestyle Factors and Professional Support
While diet is a cornerstone, achieving sustainable weight loss and optimal diabetes management involves a comprehensive approach that extends beyond what’s on your plate. Lifestyle factors and professional guidance are critical components of your success.
* Integrate regular physical activity into your routine: Exercise is not just about burning calories; it’s a powerful tool for improving insulin sensitivity, boosting metabolism, and enhancing overall well-being for diabetics.
* Cardiovascular exercise: Activities like brisk walking, jogging, cycling, swimming, or dancing help improve heart health, burn calories, and can lower blood sugar levels immediately after a workout. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, spread out over several days.
* Strength training: Lifting weights, using resistance bands, or doing bodyweight exercises (like squats, push-ups) builds and maintains muscle mass. More muscle means a higher resting metabolism, which aids in fat loss, and importantly, muscles are more efficient at absorbing glucose from the bloodstream, directly improving insulin sensitivity. Aim for 2-3 sessions per week on non-consecutive days.
* Practical tips: Find activities you enjoy to make it sustainable. Start slow and gradually increase intensity and duration. Consult your doctor before starting any new exercise program, especially if you have complications or are taking medications that affect blood sugar.
* Prioritize sufficient sleep and stress management techniques: These often-overlooked factors have a profound impact on weight, hormones, and blood sugar control.
* Sleep: Lack of sleep disrupts hunger-regulating hormones – ghrelin (which increases appetite) and leptin (which signals fullness). Poor sleep also increases cortisol (a stress hormone), which can lead to insulin resistance and fat storage, particularly around the abdomen. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Establish a consistent sleep schedule and create a relaxing bedtime routine.
* Stress management: Chronic stress, like insufficient sleep, elevates cortisol levels, negatively impacting blood sugar and promoting weight gain. Finding healthy ways to manage stress is crucial.
* Techniques: Incorporate mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, spending time in nature, listening to calming music, or engaging in hobbies you enjoy. These practices can lower cortisol, improve mood, and help you make healthier choices.
* Always consult with your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian before making significant dietary changes: This is paramount for anyone managing diabetes. Your individual needs, medications (especially insulin or other blood sugar-lowering drugs), and existing health conditions must be taken into account.
* Why professional guidance is essential:
* Safety: Your healthcare team can ensure any dietary changes are safe and won’t lead to dangerous blood sugar lows (hypoglycemia) or interfere with your medications.
* Effectiveness: A registered dietitian specializing in diabetes can create a personalized meal plan tailored to your specific carbohydrate needs, preferences, and lifestyle, maximizing your chances of successful and sustainable weight loss while improving blood sugar control.
* Monitoring: They can help you monitor your progress, adjust your plan as needed, and provide ongoing support and education. Working with an endocrinologist or a Certified Diabetes Care and Education Specialist can also provide valuable insights into medication adjustments and overall diabetes management strategies.
Achieving sustainable weight loss as a diabetic requires a holistic approach, blending thoughtful dietary choices with supportive lifestyle habits. By focusing on whole, unprocessed foods, carefully managing carbohydrate intake, embracing lean proteins and healthy fats, and staying consistent with meal planning and regular exercise, you can significantly improve your health outcomes. Remember, personalized guidance from medical professionals is paramount to developing a safe, effective, and tailored strategy for your unique journey towards better health and a more vibrant life. Take it one step at a time, celebrate your small victories, and commit to nurturing your body for the long term.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best overall diet approach for diabetics looking to lose weight?
The most effective diet approach for diabetics aiming to lose weight is typically a balanced, sustainable plan rich in whole, unprocessed foods. This means prioritizing non-starchy vegetables, lean proteins, healthy fats, and controlled portions of complex carbohydrates. Focusing on a moderate calorie deficit while ensuring nutrient density is key to supporting both weight loss and optimal blood sugar management.
How do carbohydrates impact weight loss for individuals with diabetes, and which types are best?
Carbohydrates significantly influence both blood sugar levels and weight loss for diabetics. Consuming too many refined carbohydrates can lead to blood sugar spikes and hinder weight loss by promoting fat storage. For effective weight loss, it’s best to limit simple carbs and sugary drinks, instead prioritizing complex carbohydrates from whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables, which are high in fiber and promote satiety.
Why is weight loss particularly beneficial for managing diabetes, beyond just improved appearance?
Losing weight offers profound health benefits for diabetics that extend far beyond aesthetics, primarily by improving insulin sensitivity. Even a modest weight reduction can significantly lower A1c levels, potentially reduce the need for diabetes medication, and decrease the risk of serious complications like heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage. Effective weight management is a cornerstone of long-term diabetes control and overall well-being.
Which specific foods should diabetics prioritize for effective weight loss and blood sugar control?
Diabetics should prioritize foods that are low in glycemic index, high in fiber, and rich in lean protein to simultaneously support weight loss and stable blood sugar. This includes an abundance of non-starchy vegetables (e.g., leafy greens, broccoli, bell peppers), lean protein sources (e.g., chicken breast, fish, tofu, eggs), and healthy fats (e.g., avocados, nuts, olive oil). These choices promote fullness and help regulate glucose levels efficiently.
Are low-carb or ketogenic diets safe and effective for diabetics aiming for significant weight loss?
Low-carb and ketogenic diets can be highly effective for weight loss and improving blood sugar control in many diabetics, often leading to enhanced insulin sensitivity and reduced medication requirements. However, these restrictive eating plans necessitate careful planning and must be undertaken under medical supervision, especially for those on insulin or other diabetes medications, to prevent potential complications like hypoglycemia. They are not suitable or sustainable for every individual with diabetes.
References
- Weight Loss and Diabetes: Tips for Healthy Living & Better Management
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/weight-management/adult-overweight-obesity/type-2-diabetes
- Weight loss: 6 strategies for success – Mayo Clinic
- Diabetes diet: Create your healthy-eating plan – Mayo Clinic
- https://health.clevelandclinic.org/weight-loss-and-diabetes-a-powerful-connection/
- https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/managing/healthy-eating.html


