For individuals managing diabetes, the best food choices revolve around a balanced diet rich in whole, unprocessed ingredients that help regulate blood sugar levels. This means prioritizing lean proteins, healthy fats, complex carbohydrates, and an abundance of fiber-rich fruits and vegetables. This guide will outline the key food groups and practical strategies to help you make informed dietary decisions for better health and blood sugar management.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Diabetic Eating

Managing diabetes effectively starts with a solid understanding of how food impacts your body. It’s not about deprivation, but about making smart, informed choices that keep your blood sugar steady and your body nourished.
* Focus on foods with a low glycemic index to minimize blood sugar spikes. The Glycemic Index (GI) is a system that ranks carbohydrate-containing foods by how much they raise blood sugar levels after eating. Foods with a low GI (55 or less) are digested and absorbed more slowly, leading to a gradual rise in blood sugar. Think of steel-cut oats, most non-starchy vegetables, legumes, and many fruits. High GI foods, like white bread, sugary cereals, and processed snacks, cause rapid spikes, which can be detrimental over time. By opting for low-GI choices, you help prevent these sharp fluctuations, supporting more stable blood glucose levels throughout the day.
* Balance macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, fats) at each meal. Creating balanced meals is a cornerstone of diabetic eating. Carbohydrates are the primary nutrient that impacts blood sugar, but proteins and fats play crucial supporting roles. Including a source of lean protein and healthy fat with your carbohydrates helps slow down digestion and the absorption of glucose into your bloodstream. This creates a more sustained energy release and prevents sudden blood sugar surges. Aim for a plate that visually includes a good portion of non-starchy vegetables, a modest serving of lean protein, and a controlled portion of complex carbohydrates, along with a touch of healthy fats.
* Emphasize portion control to manage caloric intake and carbohydrate load effectively. Even healthy foods can impact blood sugar if consumed in excess. Portion control is absolutely vital for managing diabetes, as it directly influences your total carbohydrate intake per meal and your overall caloric consumption. Understanding standard serving sizes for different food groups helps you accurately track your carbohydrate load, which is a key factor in predicting blood sugar responses. Using measuring cups and scales initially, or simply learning to eyeball appropriate portions, can make a huge difference in achieving stable blood sugar and maintaining a healthy weight, both critical for diabetes management.
Nutrient-Rich Non-Starchy Vegetables
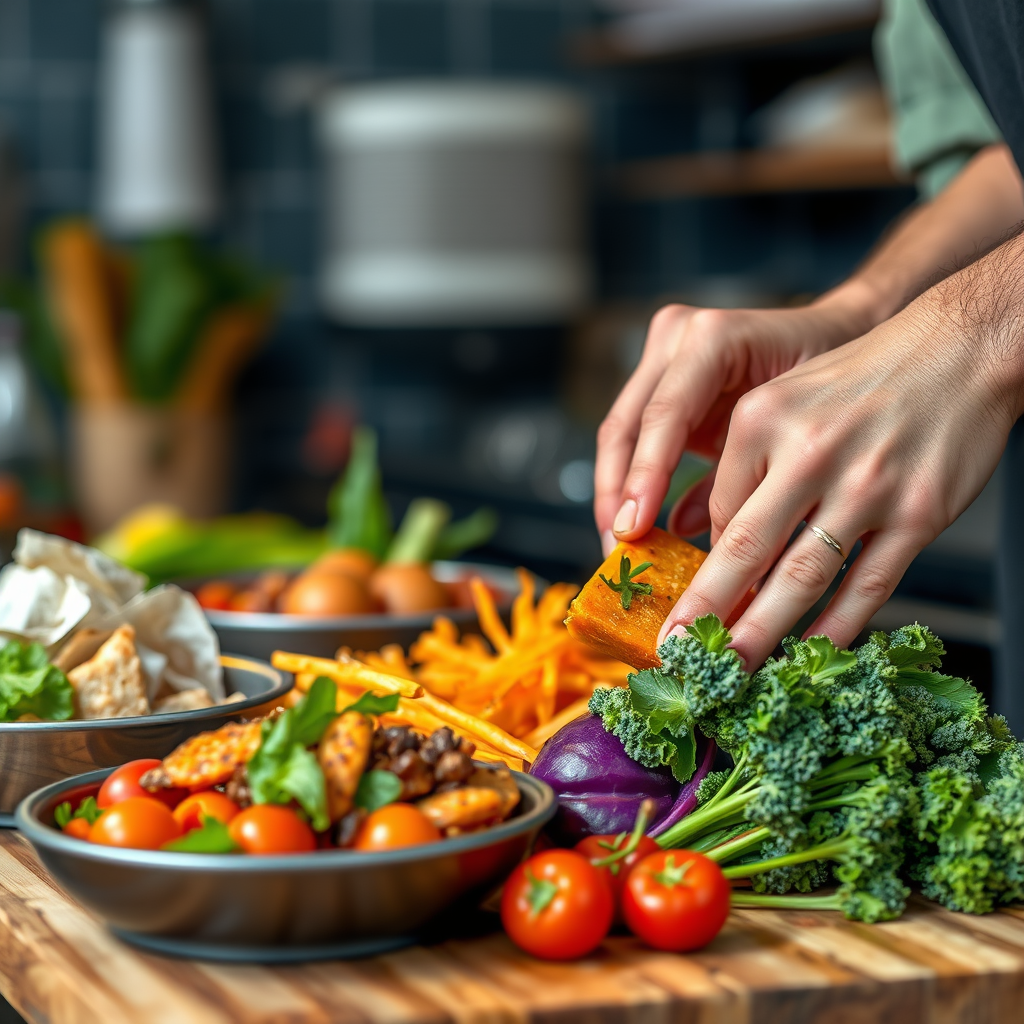
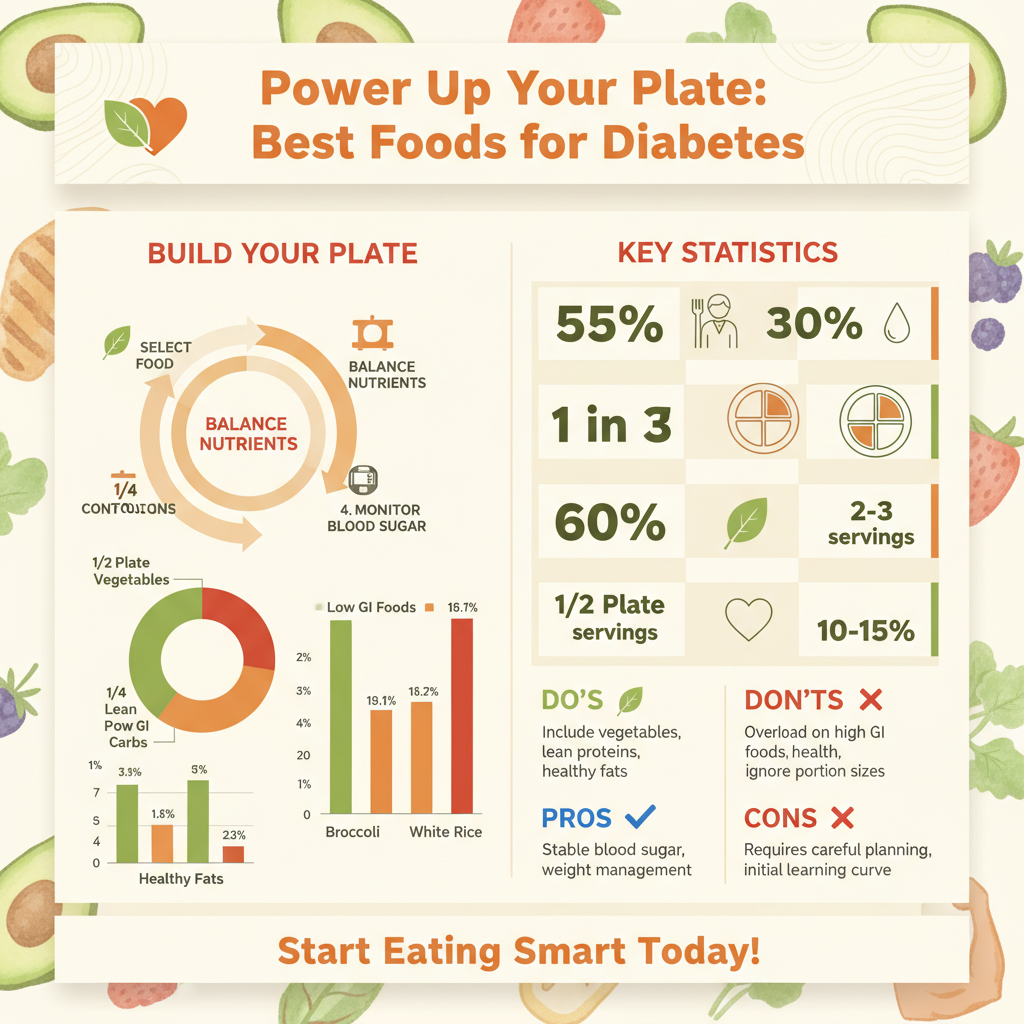

These vibrant additions should be the superstars of your plate, offering maximum nutrition with minimal impact on blood sugar.
* Examples include leafy greens (spinach, kale), broccoli, bell peppers, and asparagus. The list of non-starchy vegetables is wonderfully long and varied! Beyond these popular choices, consider Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, green beans, mushrooms, onions, tomatoes, zucchini, and cucumbers. Each offers unique flavors and textures, making it easy to incorporate a wide array into your daily meals. They are incredibly versatile and can be steamed, roasted, grilled, stir-fried, or added raw to salads.
* Packed with fiber, vitamins, and minerals; very low in carbohydrates and calories. This is where non-starchy vegetables truly shine. Their high fiber content is a game-changer for people with diabetes. Fiber not only aids digestion but also helps slow the absorption of sugar, contributing to more stable blood glucose levels. Plus, they’re loaded with essential vitamins (like Vitamin C, K, and folate) and minerals (potassium, magnesium) that support overall health, boost immunity, and provide antioxidants to protect your cells from damage, all without significantly raising your carbohydrate count or adding excess calories.
* Essential for satiety and overall health without significantly impacting blood sugar levels. Because they are so rich in fiber and water, non-starchy vegetables fill you up without filling you out. This means you can enjoy generous portions, feeling satisfied and less prone to overeating or snacking on less healthy options. Their nutritional density supports everything from heart health to bone strength, making them indispensable for anyone looking to manage diabetes while promoting vibrant health across the board. Try to fill half your plate with these amazing veggies at every meal!
Lean Proteins for Blood Sugar Stability

Protein is a powerhouse nutrient for anyone, but especially for those managing diabetes, as it plays a significant role in satiety and blood sugar control.
* Include sources like skinless poultry, fish, eggs, beans, lentils, and tofu. Diverse your protein sources to get a full spectrum of nutrients. Skinless chicken breast, turkey, and lean cuts of beef or pork are excellent animal-based options. For fish, focus on fatty varieties like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, alongside leaner options like cod and tilapia. Eggs are incredibly versatile and nutrient-dense. Plant-based proteins like chickpeas, black beans, kidney beans, and lentils are not only packed with protein but also boast significant fiber content. Tofu, tempeh, and edamame are also fantastic choices for plant-based eaters.
* Helps slow down glucose absorption, promoting a feeling of fullness and stable blood sugar. When you eat protein alongside carbohydrates, your digestive system works harder to break everything down. This extended digestion time means that glucose enters your bloodstream more gradually, preventing the rapid spikes that can occur with carb-only meals. The feeling of fullness, or satiety, that protein provides is also invaluable; it helps reduce hunger pangs and the temptation to snack on unhealthy foods between meals, which further contributes to better blood sugar management.
* Crucial for muscle maintenance and supporting various bodily functions. Beyond blood sugar, protein is fundamental for countless bodily processes. It’s the building block for muscles, skin, hair, and enzymes, and plays a critical role in immune function. Maintaining adequate muscle mass is particularly important, as muscles help utilize glucose from the bloodstream, contributing to better insulin sensitivity. Regular intake of lean protein supports your overall metabolic health and keeps your body strong and functioning optimally.
Smart Carbohydrate Choices: Whole Grains & Legumes
Carbohydrates are not off-limits for diabetics; the key is choosing the right kind that offers sustained energy without the roller coaster of blood sugar spikes.
* Opt for complex carbohydrates such as oats, quinoa, brown rice, and whole-wheat pasta. These are your go-to carbohydrate sources. Unlike their refined counterparts, complex carbohydrates retain their natural fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Oats (especially steel-cut or rolled oats), quinoa (a complete protein!), brown rice, farro, barley, and whole-wheat pasta are fantastic choices. They provide the necessary energy your body needs without causing a dramatic surge in blood sugar. When shopping, always look for “100% whole grain” on the label.
* High in fiber, these foods provide a steady, gradual release of energy, preventing sharp blood sugar rises. The high fiber content in whole grains and legumes is their superpower. Soluble fiber helps slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, while insoluble fiber adds bulk and aids digestion. This ensures that energy is released slowly and steadily, keeping you feeling full longer and preventing the energy crashes and subsequent hunger that often follow high-sugar or refined carb meals. This sustained energy is not just good for your blood sugar, but also for your mood and concentration!
* Avoid refined grains, white bread, and sugary cereals, which can cause rapid glucose spikes. This is where discernment is crucial. Refined grains, like white bread, white rice, pasta made from enriched flour, and most breakfast cereals (even many labeled “healthy”), have been stripped of their bran and germ, losing valuable fiber and nutrients. Without this fiber, they are quickly broken down into glucose, leading to rapid and significant blood sugar spikes. Making the switch to whole-grain alternatives is one of the most impactful dietary changes you can make for better blood sugar control and overall health.
Healthy Fats for Heart Health
Don’t shy away from fats entirely! The right kinds of fats are essential for good health, particularly for your heart, and can even help with diabetes management.
* Incorporate monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats from avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. These “good” fats are crucial for a healthy diet. Monounsaturated fats (MUFAs) are found abundantly in avocados, olive oil, and nuts like almonds, pecans, and cashews. Polyunsaturated fats (PUFAs) are found in walnuts, sunflower seeds, flax seeds, chia seeds, and fatty fish (like salmon and tuna), which are rich in omega-3s. These fats are linked to a reduced risk of heart disease, a common complication for individuals with diabetes.
* Crucial for heart health and can improve insulin sensitivity, a key factor in diabetes management. Healthy fats play a vital role in maintaining cardiovascular health by helping to lower bad cholesterol (LDL) and raise good cholesterol (HDL). Beyond this, studies suggest that consuming healthy fats can improve insulin sensitivity, meaning your body’s cells become more responsive to insulin, which helps regulate blood sugar more effectively. This is incredibly beneficial for people with diabetes or those at risk.
* Contributes to satiety, reducing the urge to snack on unhealthy, high-carb options. Just like protein, healthy fats are excellent at promoting satiety. They take longer to digest, keeping you feeling full and satisfied after meals. This prolonged feeling of fullness can significantly reduce cravings for sugary snacks and highly processed carbohydrates, helping you stick to your healthy eating plan and manage your overall caloric and carbohydrate intake more effectively. Remember to consume even healthy fats in moderation due to their high caloric density.
Mindful Fruit Consumption
Fruits are nature’s candy, packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. While they contain natural sugars, they can certainly be part of a diabetic-friendly diet when consumed wisely.
* Choose whole fruits (especially berries, apples, pears) over fruit juices, which lack fiber. This is a critical distinction. Whole fruits come with their natural fiber intact, which helps slow down the absorption of fructose (fruit sugar) into your bloodstream. Berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries), apples, pears, and oranges are particularly good choices due to their high fiber content and relatively lower glycemic impact. Fruit juices, on the other hand, remove most of this beneficial fiber, leading to a rapid influx of sugar that can spike blood glucose levels much more quickly than eating the whole fruit itself. Always opt for the whole fruit!
* Enjoy fruits in moderation, as they contain natural sugars that can still affect blood glucose. While whole fruits are healthy, it’s important to remember they still contain carbohydrates in the form of natural sugars. Overindulging can still lead to elevated blood sugar. A good strategy is to stick to one or two servings per day and monitor how different fruits affect your individual blood glucose levels. Pairing fruit with a source of protein or healthy fat (like a handful of nuts or Greek yogurt) can also help further mitigate any potential blood sugar spikes.
* Their natural fiber content helps mitigate the impact on blood sugar compared to processed sweets. The fiber in whole fruits isn’t just a bonus; it’s a game-changer. It acts as a natural buffer, preventing the rapid sugar surge you’d get from a piece of candy or a sugary dessert. This means you can enjoy the sweetness and nutritional benefits of fruit without the dramatic blood sugar roller coaster often associated with processed sugary foods. It’s all about making smart swaps and enjoying nature’s treats thoughtfully.
Foods to Limit and Avoid
Just as important as knowing what to eat is understanding which foods can hinder your diabetes management and overall health. Making conscious efforts to limit or eliminate these items will significantly improve your outcomes.
* Steer clear of sugary beverages, candies, pastries, and highly processed snacks. These items are often laden with added sugars, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats, offering little to no nutritional value. Sugary drinks like sodas, sweetened teas, and fruit punches cause immediate and dramatic blood sugar spikes, providing empty calories that contribute to weight gain. Candies, cookies, cakes, and pastries deliver a similar sugar rush. Highly processed snacks (like chips, crackers made from refined flour, and many breakfast bars) are often high in unhealthy fats, sodium, and hidden sugars, leading to poor blood sugar control and an increased risk of other health issues.
* Reduce intake of saturated fats found in fried foods, fatty meats, and full-fat dairy. While healthy fats are beneficial, saturated and trans fats can be detrimental, especially for heart health, which is a major concern for individuals with diabetes. Saturated fats, commonly found in fatty cuts of red meat, processed meats (like bacon and sausage), butter, full-fat dairy products, and many fried foods, can raise LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels. Trans fats, often found in partially hydrogenated oils in baked goods and fast food, are even worse for heart health. Limiting these fats helps protect your cardiovascular system and can improve insulin sensitivity.
* Minimize refined grains and foods with added sugars to maintain stable blood glucose and promote cardiovascular health. This reinforces the earlier point about smart carbohydrate choices. Beyond pastries and candies, many everyday foods contain surprisingly high amounts of refined grains and added sugars, from white bread and bagels to breakfast cereals and condiments. Always read food labels carefully! Reducing your intake of these items is crucial for preventing erratic blood sugar levels and achieving long-term stability. By making these changes, you’re not just managing your diabetes; you’re actively promoting a healthier heart and a more energetic, vibrant life.
Adopting a diet focused on whole, unprocessed foods, lean proteins, healthy fats, and fiber-rich carbohydrates is paramount for managing diabetes effectively. By making conscious food choices and understanding how different foods impact your blood sugar, you can achieve better health outcomes and improve your quality of life. This approach empowers you to take control of your health with delicious, nourishing meals. Always consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to create a personalized meal plan tailored to your specific needs and health goals, ensuring your dietary changes are safe and effective for your unique situation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the best types of foods for a diabetic diet to help manage blood sugar?
The best foods for a diabetic diet focus on whole, unprocessed options that help stabilize blood sugar levels. Prioritize lean proteins, healthy fats, fiber-rich fruits and non-starchy vegetables, and complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index. These nutrient-dense foods provide sustained energy, promote satiety, and minimize the risk of sharp blood sugar spikes, forming the foundation of healthy eating for diabetics.
How can I effectively choose carbohydrates that are safe for diabetics?
When choosing carbohydrates for a diabetic diet, opt for complex carbs rich in fiber over refined options. Focus on whole grains like oats, brown rice, quinoa, and whole-wheat bread, along with legumes such as beans and lentils. These choices have a slower, more gradual impact on blood glucose, providing sustained energy and supporting better blood sugar control compared to the quick-releasing sugars found in processed foods.
Why is incorporating lean protein and healthy fats crucial for people with diabetes?
Lean protein and healthy fats are crucial for individuals with diabetes because they help slow down sugar absorption, promote satiety, and prevent overeating, which in turn helps manage blood sugar spikes. Protein sources like chicken, fish, tofu, and legumes, along with healthy fats from avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, contribute to stable energy levels and support overall metabolic health. This combination is vital for weight management and improving insulin sensitivity, key aspects of diabetes care.
Which fruits and vegetables are most recommended for individuals with diabetes?
For individuals with diabetes, non-starchy vegetables like leafy greens (spinach, kale), broccoli, bell peppers, and cucumbers are highly recommended due to their low calorie and carbohydrate content and high fiber. Regarding fruits, berries, apples, citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruits), and kiwis are excellent choices in moderation, as they offer essential vitamins, antioxidants, and fiber with a relatively lower glycemic impact compared to tropical fruits. Always monitor portion sizes for fruits to maintain optimal blood sugar levels.
What common foods should diabetics limit or avoid to prevent blood sugar spikes?
To prevent harmful blood sugar spikes, diabetics should significantly limit or avoid highly processed foods, sugary drinks, refined grains, and unhealthy fats. This includes items like sodas, fruit juices with added sugar, white bread, pastries, sugary cereals, candy, fried foods, and anything high in trans fats. These foods can rapidly elevate blood glucose levels, making diabetes management challenging and increasing the risk for long-term health complications.
References
- What superstar foods are good for diabetes? | ADA
- https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/managing/healthy-eating.html
- Healthy Living with Diabetes – NIDDK
- Diabetes diet: Create your healthy-eating plan – Mayo Clinic
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/diseases-and-conditions/diabetes-a-healthy-diet-is-key-to-managing-it
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/11267-diabetes-and-diet
- Diabetic Diet | MedlinePlus


