
When searching for the “best” multivitamin for diabetics, it’s crucial to understand that there isn’t one universal answer, but rather a set of critical criteria. The most effective multivitamins for individuals with diabetes are those specifically formulated to support blood sugar regulation and prevent common nutrient deficiencies, often characterized by the absence of added sugars, appropriate levels of B vitamins, vitamin D, magnesium, and chromium, and third-party verification. This guide will help you navigate the options to make an informed choice.
Why Multivitamins Are Important for Diabetics
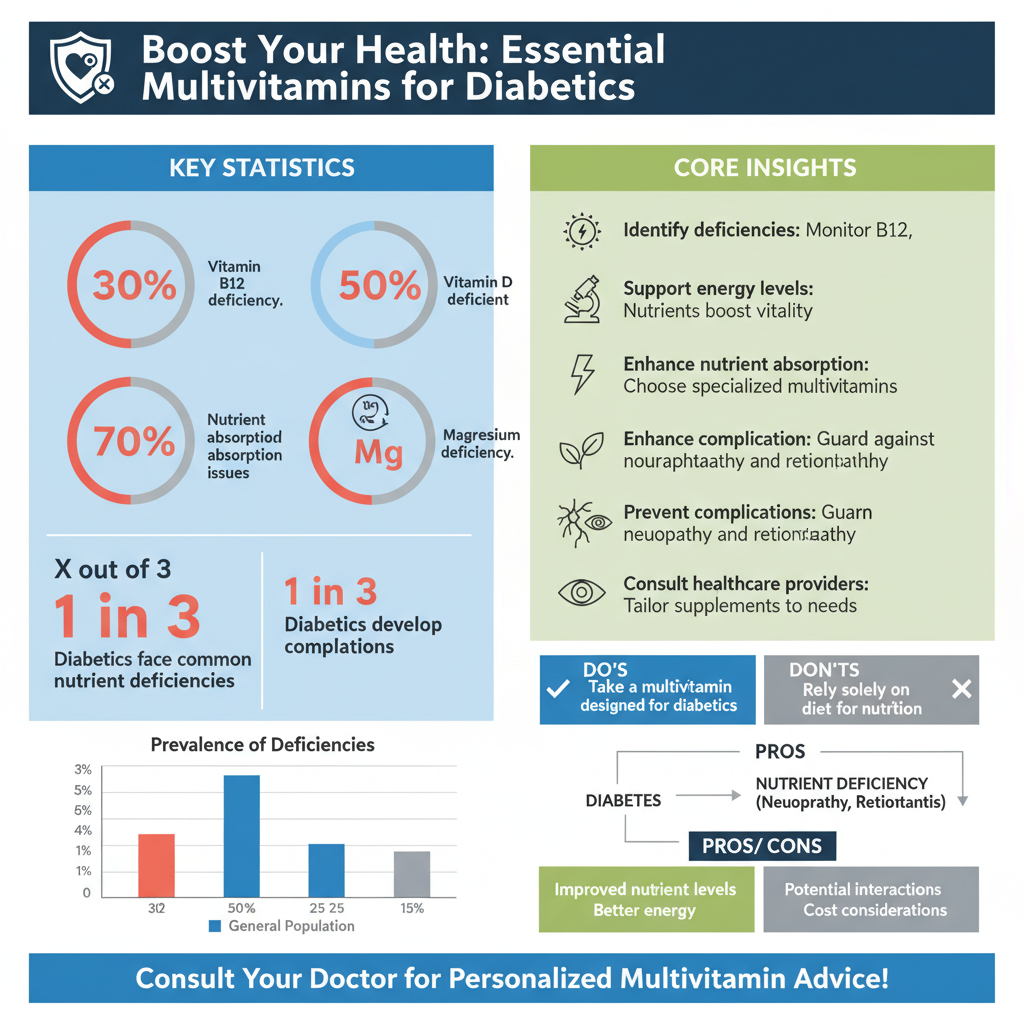

Living with diabetes is a journey that often requires careful attention to diet, lifestyle, and medication. While a balanced diet is always the cornerstone of good health, sometimes it’s not enough to meet all your nutritional needs, especially when managing a chronic condition like diabetes. This is where a well-chosen multivitamin can play a supportive role, acting as a nutritional safety net.
– Diabetes and certain medications (like metformin) can interfere with nutrient absorption and increase excretion, leading to deficiencies.
Diabetes itself can alter how your body processes and utilizes nutrients. For example, high blood sugar levels can lead to increased urination, which can flush out essential water-soluble vitamins and minerals. Furthermore, a very common and effective medication for type 2 diabetes, metformin, is known to specifically interfere with the absorption of vitamin B12. This can lead to a significant deficiency over time, potentially impacting nerve health and energy levels. Other medications might also have similar effects, making it a real challenge to maintain optimal nutrient status through diet alone.
– Maintaining optimal nutrient levels can support overall health, energy, and help manage diabetes-related complications.
Beyond just preventing deficiencies, ensuring your body has adequate levels of key nutrients can have a profound impact on your overall well-being. Optimal nutrient intake can help improve energy levels, support immune function, and contribute to better blood sugar control by supporting insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Importantly, proper nutrition can also play a preventative role in reducing the risk of long-term diabetes-related complications, such as neuropathy (nerve damage), retinopathy (eye damage), nephropathy (kidney damage), and cardiovascular issues. Think of it as giving your body the best tools to fight back.
– Common deficiencies in diabetics include Vitamin B12, Vitamin D, Magnesium, and Zinc.
Research consistently shows that individuals with diabetes are more prone to certain nutrient deficiencies compared to the general population. As mentioned, Vitamin B12 deficiency is common, particularly for those on metformin. Vitamin D deficiency is also widespread among diabetics and has significant implications for bone health and insulin sensitivity. Magnesium, crucial for over 300 bodily functions, including glucose metabolism and nerve function, is often found at lower levels in diabetics due to increased urinary excretion. Zinc, important for immune function and insulin synthesis, can also be suboptimal. Addressing these specific gaps is a key reason why a targeted multivitamin can be so beneficial.
Essential Nutrients for Diabetics to Prioritize

When you’re looking for a multivitamin, it’s not just about a broad spectrum of nutrients, but rather a targeted approach to those that are most beneficial and commonly deficient for individuals with diabetes.
– B Vitamins (especially B12 and B1): Crucial for nerve health and energy metabolism; B12 deficiency is common with metformin use.
The B-vitamin complex is like a powerhouse for your body’s energy production. For diabetics, B1 (thiamine) is particularly vital because it helps prevent the formation of Advanced Glycation End-products (AGEs), which contribute to diabetic complications like neuropathy. B12 (cobalamin) is absolutely critical for healthy nerve function and red blood cell production. As we discussed, if you’re taking metformin, your risk of B12 deficiency is significantly higher. Look for a multivitamin that includes sufficient levels of B1 (often as benfotiamine, a more bioavailable form) and B12, ideally in its active form, methylcobalamin, which is better absorbed and utilized by the body.
– Vitamin D: Plays a role in bone health, immune function, and has been linked to insulin sensitivity.
Often called the “sunshine vitamin,” Vitamin D is far more than just for bone health. It plays a significant role in modulating your immune system, reducing inflammation, and importantly for diabetics, it’s been linked to insulin sensitivity and pancreatic beta-cell function. Many people, including a high percentage of those with diabetes, are deficient in Vitamin D. Ensuring adequate levels (often measured as 25(OH)D in blood tests) can support better glucose control and overall well-being. Aim for Vitamin D3, which is the most effective form for raising blood levels.
– Magnesium: Important for glucose metabolism, nerve function, and blood pressure regulation, often low in diabetics.
Magnesium is an unsung hero! It’s involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions in your body, many of which are directly related to glucose control, insulin signaling, and energy production. Low magnesium levels are common in diabetics, partly due to increased urinary excretion caused by high blood sugar. Adequate magnesium can help improve insulin sensitivity, stabilize blood sugar, support nerve and muscle function, and even help regulate blood pressure – a common concern for diabetics. Look for highly absorbable forms like magnesium citrate, glycinate, or malate.
– Chromium: May enhance insulin action and improve glucose utilization, supporting blood sugar control.
Chromium is a trace mineral that has gained attention for its potential role in glucose metabolism. It’s believed to enhance the action of insulin, helping your body use glucose more effectively. While research on chromium’s impact on blood sugar control in diabetics has shown mixed results, some studies suggest it may be beneficial for certain individuals, particularly those with chromium deficiency. If you choose a multivitamin with chromium, look for forms like chromium picolinate, which is considered more bioavailable.
What to Avoid in Diabetic Multivitamins
Just as important as knowing what to include, is understanding what to steer clear of when selecting a multivitamin for diabetes. You want a supplement that supports your health goals, not hinders them.
– Added Sugars and Artificial Sweeteners: These can counteract efforts to manage blood sugar and are unnecessary in a supplement.
It might sound counterintuitive, but some multivitamins, especially gummies, chewables, or liquid formulations, can contain added sugars or high-fructose corn syrup to improve taste. For someone managing blood sugar, this is definitely something to avoid. Even artificial sweeteners, while calorie-free, can be problematic for some individuals and may have an impact on gut microbiota, which plays a role in metabolic health. Always read the “other ingredients” list carefully and opt for sugar-free and artificial sweetener-free options.
– Excessive Doses of Certain Nutrients: High levels of some vitamins (e.g., Vitamin A, Iron unless deficient) can be harmful and should be avoided.
More is not always better, especially with supplements. Fat-soluble vitamins like Vitamin A (in its pre-formed retinol form, not beta-carotene) can accumulate in the body to toxic levels. For iron, while it’s essential, excessive amounts can be pro-oxidative, potentially worsening insulin resistance and increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease. Unless you have a diagnosed iron deficiency (confirmed by blood tests), multivitamins for diabetics should either be iron-free or contain only very modest amounts. Always consult your doctor before taking high doses of any specific nutrient.
– Unnecessary Fillers, Dyes, or Artificial Flavors: Opt for cleaner formulas to minimize potential allergens or unwanted additives.
Many supplements contain a host of inactive ingredients like binders, fillers, preservatives, artificial colors (e.g., “Red 40,” “Yellow 5”), and artificial flavors to make them look or taste better, or to aid in manufacturing. These offer no nutritional benefit and, for some sensitive individuals, can trigger allergic reactions or digestive upset. Look for brands that prioritize transparency and minimal “other ingredients,” opting for clean, hypoallergenic formulas. Natural flavors derived from plants are generally a better choice if flavors are present at all.
Key Considerations for Choosing a Multivitamin
Beyond the nutrient profile, the quality and formulation of the multivitamin are paramount. You want to ensure you’re getting what the label promises, in a form your body can actually use.
– Third-Party Testing & Certifications: Look for seals from organizations like USP Verified or NSF Certified to ensure purity, potency, and label accuracy.
The supplement industry is not as strictly regulated as the pharmaceutical industry, which means product quality can vary widely. This is why third-party testing is so crucial. Organizations like USP (United States Pharmacopeia) and NSF International independently verify that a supplement contains the ingredients listed on its label, in the declared amounts, and is free from harmful contaminants like heavy metals, pesticides, and microbes. A seal from one of these reputable bodies provides an extra layer of assurance that you’re getting a safe, high-quality product that lives up to its claims.
– Diabetic-Specific Formulations: Many brands offer multivitamins tailored for diabetics, which balance nutrient levels appropriately.
To simplify your search and ensure you’re getting a thoughtful nutrient balance, consider multivitamins specifically marketed for individuals with diabetes. These formulations are typically designed with your unique needs in mind, often featuring higher levels of B vitamins, vitamin D, magnesium, and chromium, while either omitting iron or including it in very conservative amounts (unless otherwise indicated). They take the guesswork out of crafting your own nutrient cocktail and provide targeted support for blood sugar management and common diabetic deficiencies.
– Bioavailability of Nutrients: Consider the forms of vitamins and minerals for better absorption (e.g., methylcobalamin for B12, magnesium citrate).
It’s not just about what nutrients are in your multivitamin, but also how your body can use them. Different forms of the same vitamin or mineral can have vastly different rates of absorption and utilization (this is called bioavailability). For example, as mentioned, methylcobalamin is a more active and bioavailable form of B12 than cyanocobalamin. For folate, look for L-methylfolate rather than folic acid, especially if you have genetic variations that impair folate metabolism. For minerals, chelated forms (like zinc picolinate, magnesium glycinate, or chromium picolinate) are generally better absorbed than their oxide or carbonate counterparts. Opting for bioavailable forms ensures your body can actually put those valuable nutrients to work.
Potential Benefits of the Right Multivitamin
When you choose a multivitamin wisely, aligning it with your specific diabetic needs, you open the door to several potential health advantages that can significantly complement your overall diabetes management plan.
– Support for Blood Sugar Management: By addressing nutrient gaps that impact insulin function and glucose metabolism.
A well-chosen multivitamin can be a powerful ally in your quest for stable blood sugar. Nutrients like magnesium, chromium, and vitamin D play direct roles in insulin signaling, glucose uptake into cells, and the overall efficiency of your body’s glucose metabolism. By ensuring you have adequate levels of these crucial players, you’re essentially providing your body with the building blocks it needs to utilize insulin more effectively and process sugar more efficiently, potentially leading to more stable glucose levels and improved A1c over time.
– Reduced Risk of Complications: Adequate nutrient intake can help mitigate risks associated with nerve damage, cardiovascular health, and bone density.
One of the most concerning aspects of diabetes is the long-term risk of complications. The right multivitamin can offer protective benefits by supporting various bodily systems. For instance, sufficient B vitamins are vital for nerve health and can help reduce the risk of diabetic neuropathy. Magnesium and Vitamin D contribute to cardiovascular health and help maintain healthy blood pressure. Vitamin D is also critical for bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis, which can be a concern for some diabetics. By proactively addressing nutrient deficiencies, you’re strengthening your body’s defenses against these potential long-term issues.
– Improved Energy and Well-being: Correcting deficiencies can lead to better energy levels and overall vitality.
Feeling chronically fatigued is a common complaint among individuals with diabetes. Deficiencies in key nutrients like B vitamins (essential for energy production), Vitamin D (linked to fatigue and mood), and magnesium (important for muscle function and sleep quality) can all contribute to a general lack of energy and vitality. By correcting these nutritional gaps with a targeted multivitamin, many people experience a noticeable boost in energy, improved mood, and an overall enhanced sense of well-being, making it easier to maintain an active lifestyle and engage in daily activities.
Consulting Your Healthcare Provider
While it’s exciting to explore ways to enhance your health, the most important step in choosing any supplement, especially when managing a condition like diabetes, is always to bring your healthcare team into the conversation.
– Always discuss any new supplements with your doctor or a registered dietitian before starting.
This isn’t just a recommendation; it’s a critical safety measure. Your doctor or a registered dietitian who specializes in diabetes care has a comprehensive understanding of your health history, current medications, and specific needs. They can provide personalized advice that you won’t get from even the most well-researched blog post. Think of them as your personal health navigators.
– They can assess your individual needs, check for existing deficiencies, and ensure no interactions with current medications.
A healthcare professional can order blood tests to pinpoint any specific nutrient deficiencies you might have, allowing for a truly tailored supplement approach rather than a guessing game. Furthermore, they are experts in pharmacodynamics and can identify potential interactions between supplements and your prescription medications. For example, some supplements can interfere with blood thinners, blood pressure medications, or even the absorption of your diabetes drugs. Avoiding these interactions is paramount to your safety and the effectiveness of your diabetes management.
– A healthcare professional can help tailor your supplement regimen to your specific diabetes management plan.
Your diabetes management plan is unique to you, encompassing your diet, exercise routine, medications, and lifestyle. A healthcare provider can help integrate a multivitamin seamlessly into this plan, ensuring it complements your other efforts and doesn’t disrupt any established protocols. They can guide you on appropriate dosages, monitor your progress, and make adjustments as needed, helping you get the most benefit safely and effectively.
Choosing the right multivitamin for diabetes involves careful consideration of nutrient profiles, ingredient transparency, and personal health needs. While no single pill can replace a balanced diet and regular exercise, a well-chosen multivitamin can be a valuable tool in your diabetes management arsenal, helping to fill nutritional gaps and support overall health. Always consult with your healthcare provider to ensure the supplement aligns with your specific health requirements and medication regimen before making a decision.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do diabetics need a specialized multivitamin, rather than a standard one?
Diabetics often have unique nutritional needs and may experience deficiencies due to medication side effects (like metformin depleting B12) or the disease itself impacting nutrient absorption. A specialized multivitamin for diabetics is formulated to provide higher doses of specific vitamins and minerals crucial for nerve health, blood sugar regulation, and antioxidant protection, such as chromium, magnesium, B vitamins, and vitamin D, which might be insufficient in a standard multivitamin. This targeted approach helps address specific challenges faced by individuals managing diabetes.
What key nutrients should diabetics look for in a multivitamin?
Diabetics should prioritize multivitamins containing chromium, which plays a role in insulin sensitivity, and magnesium, essential for over 300 bodily functions including glucose metabolism. Look for adequate doses of B vitamins (especially B12, often depleted by metformin), vitamin D for bone and immune health, and antioxidants like vitamin C and E to combat oxidative stress. Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) is also a beneficial addition for nerve health.
How can a multivitamin help manage nutrient deficiencies often associated with diabetes?
Multivitamins for diabetics are designed to replenish vital nutrients that are commonly depleted due to the condition or its treatments. For instance, metformin use can lower vitamin B12 levels, leading to nerve issues, which a targeted multivitamin can counteract. By supplying essential vitamins and minerals like magnesium, vitamin D, and B-complex vitamins, these supplements help support proper nerve function, energy metabolism, and overall cellular health, addressing common deficiencies and mitigating potential complications.
Are there any ingredients or dosages diabetics should avoid in a multivitamin?
Diabetics should be cautious of multivitamins with high sugar content or artificial sweeteners, as these can impact blood sugar levels. Avoid excessive doses of certain fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) that can accumulate and become toxic, and always check for potential interactions with existing diabetes medications. It’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement to ensure it’s safe and appropriate for your specific health needs and medication regimen.
Which factors are most important when choosing the best multivitamin for diabetics?
When selecting the best multivitamin for diabetics, prioritize formulations specifically labeled for “diabetic support” or “blood sugar health” to ensure targeted nutrient profiles. Look for third-party testing certifications (like USP or NSF) to guarantee purity and potency, and always check the ingredient list to confirm the presence of key nutrients like chromium, magnesium, B12, and vitamin D without unnecessary fillers or sugars. Consulting your doctor or a registered dietitian is paramount to tailor the choice to your individual needs and avoid contraindications.
References
- https://diabetes.org/healthy-living/medication-treatments/supplements-and-vitamins
- Laryngospasm: What causes it? – Mayo Clinic
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/diseases-and-conditions/is-there-a-place-for-supplements-in-diabetes-care
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/17393-diabetes-and-nutrition-supplements-vitamins-and-minerals
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diet-nutrition/vitamins-minerals-supplements