For individuals managing diabetes, certain teas can be beneficial additions to a healthy diet, offering natural compounds that may help regulate blood sugar, improve insulin sensitivity, and provide antioxidant support. Green tea, hibiscus, ginger, and cinnamon tea stand out as top choices due to their well-researched properties and potential positive impacts on glucose metabolism and overall well-being. This guide will explore these and other soothing teas that can contribute to a balanced diabetes management plan, helping you discover delicious ways to support your health journey.
Understanding Tea’s Role in Diabetes Management
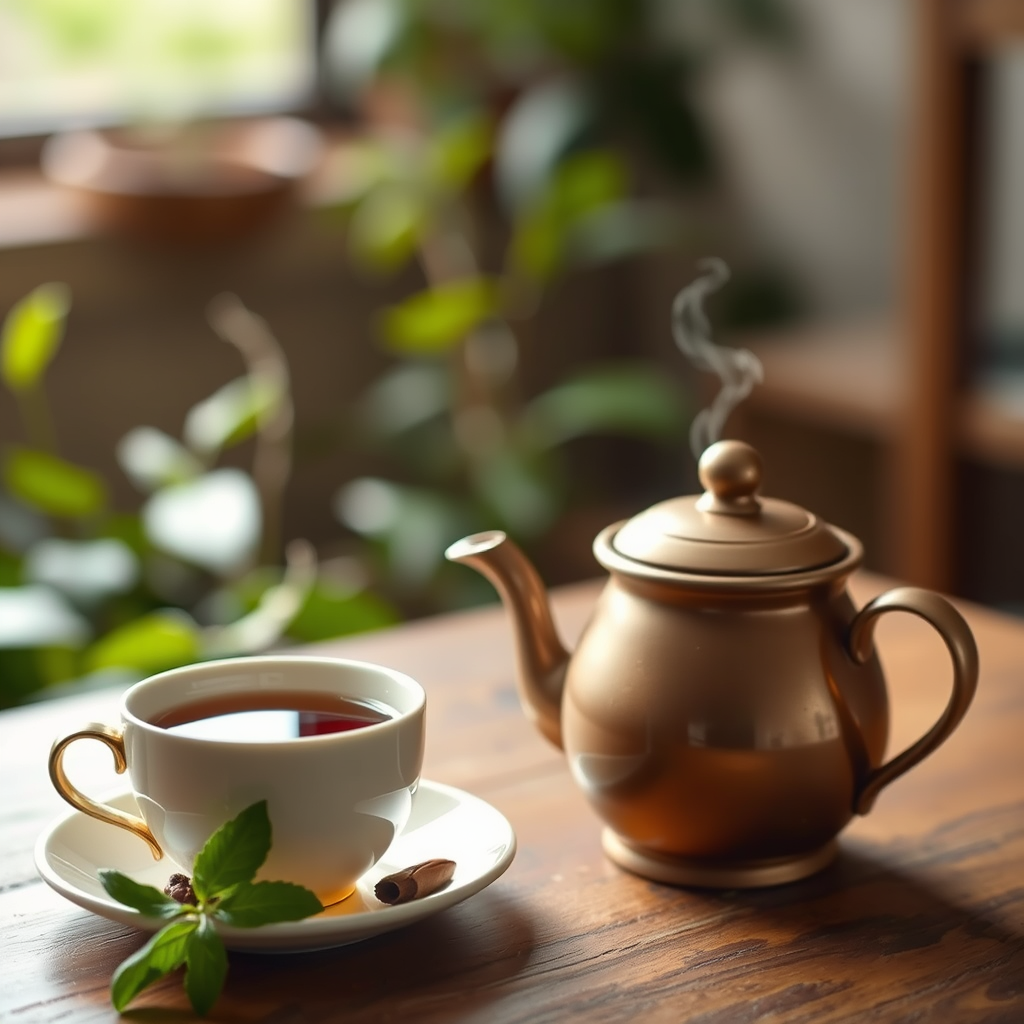

Navigating diabetes management can feel overwhelming, but sometimes, simple daily choices can make a significant difference. Incorporating specific teas into your routine is one such choice, offering a gentle yet powerful way to support your health. It’s not just about enjoying a warm beverage; it’s about harnessing the natural goodness within these ancient leaves and roots.
* Natural Compounds: Many teas are veritable treasure chests of beneficial plant compounds. They contain an array of polyphenols, flavonoids, and other bioactive substances that work synergistically within your body. These aren’t just fancy words; they represent potent antioxidants like catechins (found in green tea) and anthocyanins (in hibiscus), which combat oxidative stress – a key contributor to insulin resistance and diabetes complications. They also possess anti-inflammatory properties, helping to quell chronic inflammation often associated with metabolic dysfunction. By influencing enzymes involved in glucose production and breakdown, these compounds can subtly but effectively impact how your body handles sugar, contributing to better overall metabolic health.
* Blood Sugar Regulation: The magic of these compounds extends to directly influencing blood sugar levels. For instance, some components in certain teas may help to improve insulin sensitivity, meaning your body’s cells become more responsive to insulin, allowing glucose to enter more efficiently. Others might play a role in reducing glucose absorption from the gut after meals, preventing sharp spikes in blood sugar. There’s also research suggesting that certain teas can help lower fasting blood sugar levels, contributing to more stable glucose control throughout the day. It’s like having a natural support system that helps your body maintain balance, working alongside other healthy habits.
* Important Considerations: While the benefits of tea are exciting, it’s crucial to approach their consumption mindfully. First and foremost, always choose unsweetened teas. Adding sugar, honey, or artificial sweeteners would counteract many of the positive effects on blood sugar, essentially defeating the purpose. Secondly, remember that tea is a complementary support, not a replacement for prescribed medication, insulin, or professional medical advice. Think of it as a helpful ally in your diabetes management plan, working in harmony with your doctor’s recommendations. Always have a conversation with your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian before making significant changes to your diet, especially when managing a chronic condition like diabetes, to ensure these additions are right for you and don’t interact with any medications.
Green Tea: A Potent Ally for Glucose Control
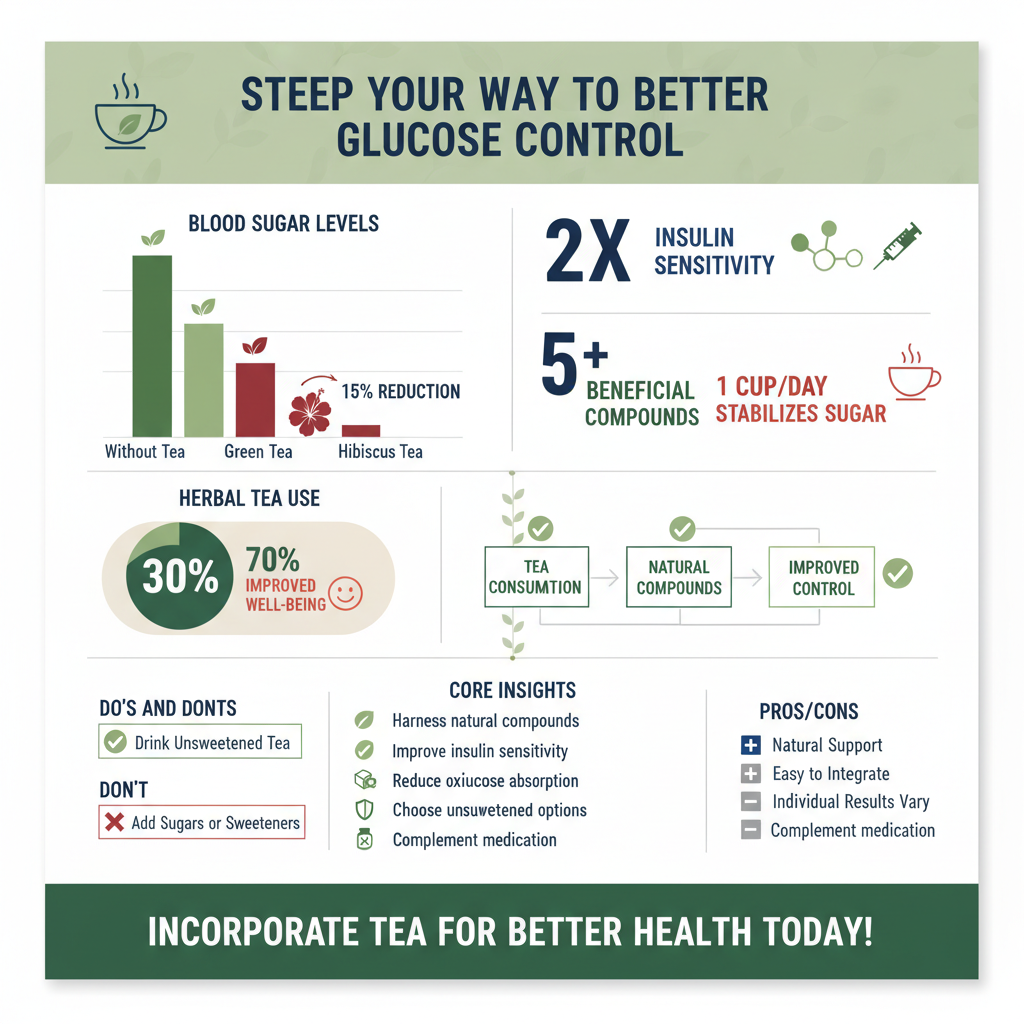

Green tea, a beloved beverage around the world, is far more than just a refreshing drink; it’s a wellness powerhouse, particularly for those focused on blood sugar management. Its unfermented nature means it retains a higher concentration of crucial compounds that can significantly benefit metabolic health.
* Rich in EGCG: The true star of green tea is epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a powerful antioxidant belonging to the catechin family. EGCG is celebrated for its ability to combat oxidative stress, which is often elevated in individuals with diabetes and can contribute to insulin resistance. By reducing cellular damage, EGCG helps improve the functioning of insulin receptors, making your cells more receptive to insulin. This enhanced sensitivity means your body can utilize glucose more efficiently, leading to better blood sugar control. Think of EGCG as a cellular guardian, protecting and optimizing the systems involved in glucose metabolism.
* Metabolic Benefits: The evidence supporting green tea’s role in metabolic health is quite compelling. Numerous studies and meta-analyses have linked regular green tea consumption to several positive outcomes for individuals with diabetes or those at risk. These benefits include a reduction in fasting blood glucose levels, a key indicator of overall glucose control. Furthermore, some research indicates that daily green tea intake can help lower HbA1c levels, which reflect average blood sugar over two to three months. These improvements are attributed not only to EGCG but also to other catechins and flavonoids that work together to modulate various metabolic pathways, potentially improving the function of pancreatic beta-cells (which produce insulin) and decreasing glucose production in the liver.
* Weight Management Support: Maintaining a healthy weight is undeniably one of the most crucial aspects of diabetes management, and green tea can offer valuable support in this area. EGCG, combined with the natural caffeine present in green tea, has been shown to gently boost metabolism and enhance fat oxidation. This means your body might burn more calories and fat, even at rest. While green tea isn’t a magic weight loss solution, consistent consumption as part of a balanced diet and active lifestyle can contribute to healthy weight management. By helping you maintain a healthier weight, green tea indirectly improves insulin sensitivity and reduces the overall burden on your glucose regulation system, making it an excellent companion on your wellness journey.
Hibiscus Tea: Beyond Blood Pressure Benefits

With its vibrant crimson hue and tart, floral flavor, hibiscus tea is a delightful sensory experience. But beyond its aesthetic appeal, this beautiful brew offers a wealth of health benefits, especially for those navigating diabetes. It’s a fantastic example of how nature provides both pleasure and potent medicine.
* Antioxidant Powerhouse: Hibiscus tea is brimming with powerful antioxidants, particularly anthocyanins, which are responsible for its striking red color. These compounds are highly effective at neutralizing free radicals in the body, which can cause oxidative stress and cellular damage. For individuals with diabetes, chronic low-grade inflammation and oxidative stress are common concerns that can exacerbate insulin resistance and contribute to complications. By providing a rich source of antioxidants, hibiscus tea acts as a protective shield, helping to reduce inflammation and safeguard your cells, thereby supporting overall health and potentially improving metabolic function.
* Blood Pressure Reduction: One of the most well-researched and celebrated benefits of hibiscus tea is its remarkable ability to help lower high blood pressure. Hypertension is a common comorbidity for people with diabetes, significantly increasing the risk of cardiovascular complications. Hibiscus tea appears to work by acting as a mild diuretic and by inhibiting the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), similar to some blood pressure medications, which helps relax blood vessels. Incorporating unsweetened hibiscus tea into your daily routine can be a natural and pleasant way to contribute to managing your blood pressure, thereby reducing your cardiovascular risk and offering a significant advantage for overall diabetes care.
* Potential Glucose Effects: While its impact on blood pressure is well-established, emerging research suggests that hibiscus tea may also play a role in directly influencing blood glucose and lipid levels. Some studies indicate that compounds in hibiscus can inhibit certain enzymes responsible for carbohydrate breakdown and absorption, which could lead to reduced post-meal blood sugar spikes. Additionally, it may help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce cholesterol levels, which are often elevated in individuals with diabetes. While more extensive human trials are needed to fully confirm these glucose-lowering effects, the initial findings are promising, making hibiscus tea an exciting area of ongoing study and a potentially beneficial addition to a diabetes-friendly diet.
Ginger Tea: Anti-inflammatory and Blood Sugar Support
Ginger, a staple in traditional medicine systems across the globe, offers more than just a zesty kick to your culinary creations. Brewed into a soothing tea, this root delivers potent medicinal properties that can be particularly helpful for individuals managing diabetes, addressing both inflammation and glucose metabolism.
* Active Compounds: The incredible health benefits of ginger stem from its primary active compounds: gingerols and shogaols. These bioactive molecules are responsible for ginger’s pungent flavor and its powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Chronic inflammation is a hallmark of many metabolic disorders, including type 2 diabetes, and can exacerbate insulin resistance. Gingerols and shogaols work by inhibiting the production of inflammatory markers in the body, effectively calming down systemic inflammation. By reducing this underlying inflammation, ginger tea can help create a more favorable environment for improved insulin sensitivity and overall cellular health.
* Glucose Metabolism: Beyond its anti-inflammatory prowess, ginger has garnered attention for its potential direct impact on glucose metabolism. Some compelling studies suggest that regular consumption of ginger can help reduce fasting blood sugar levels, a critical marker for diabetes management. The mechanisms behind this include enhancing glucose uptake into muscle cells (making them more efficient at using sugar from the bloodstream), improving insulin sensitivity, and possibly even modulating the release of insulin from the pancreas. While research is ongoing, these findings position ginger tea as a promising natural support for better blood sugar control, working to stabilize glucose levels and reduce the burden on your body’s insulin system.
* Digestive Aid: Ginger has been revered for centuries as a natural digestive aid, and this benefit can indirectly contribute to overall well-being for individuals with diabetes. It’s highly effective at soothing an upset stomach, alleviating nausea, and reducing indigestion and bloating. When your digestive system is functioning optimally, your body is better able to absorb nutrients, and you experience less discomfort, which can reduce stress. Since stress can negatively impact blood sugar levels by triggering the release of hormones like cortisol, a calm and comfortable digestive system contributes to a more stable internal environment. Enjoying a warm cup of ginger tea after meals can be a wonderfully comforting ritual that supports not just your glucose levels but your entire digestive harmony.
Cinnamon Tea: A Sweet Spice for Insulin Sensitivity
Cinnamon, with its warm, inviting aroma and subtly sweet flavor, is much more than just a spice for baking; it’s a powerful ally in the fight against insulin resistance. Brewing cinnamon into a comforting tea allows you to tap into its unique therapeutic properties, making it an excellent addition to a diabetes-friendly lifestyle.
* Insulin Mimicry: One of the most fascinating aspects of cinnamon’s impact on diabetes is its ability to mimic the actions of insulin within the body. Compounds found in cinnamon, particularly cinnamaldehyde and methylhydroxychalcone polymer (MHCP), have been shown to activate insulin receptors on cells. This means they can help cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream more efficiently, essentially acting like insulin itself or significantly enhancing insulin’s effectiveness. By improving cellular glucose uptake, cinnamon tea can help lower circulating blood sugar and reduce the demand on your pancreas to produce more insulin, offering valuable support for insulin sensitivity.
* Blood Sugar Reduction: The research on cinnamon’s effect on blood sugar levels is quite promising. Studies have indicated that incorporating cinnamon into the diet can help reduce fasting blood glucose levels and mitigate post-meal blood sugar spikes. It appears to achieve this through several mechanisms: by slowing down gastric emptying (meaning food stays in your stomach longer, leading to a slower release of glucose into the bloodstream) and by inhibiting certain enzymes that break down carbohydrates in the digestive tract. These combined actions result in a more gradual and controlled rise in blood sugar after eating, which is incredibly beneficial for preventing the rollercoaster effect of high glucose peaks.
* Type and Dosage: When it comes to cinnamon, quality and type matter significantly. There are two main types: Ceylon cinnamon (often called “true cinnamon”) and Cassia cinnamon. While both offer benefits, Ceylon cinnamon is generally preferred, especially for regular consumption, because it has significantly lower levels of coumarin. Coumarin is a natural compound that, in large doses, can be toxic to the liver. Cassia cinnamon, commonly found in most grocery stores, contains much higher levels of coumarin. Therefore, if you’re planning to regularly consume cinnamon tea for its health benefits, opt for Ceylon cinnamon for safety. Furthermore, always consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for appropriate dosage recommendations. While tea generally provides lower doses than supplements, it’s vital to ensure it aligns with your individual health needs and does not interact with any diabetes medications you may be taking.
Peppermint and Chamomile: Soothing Choices for Overall Health
While green tea, hibiscus, ginger, and cinnamon directly target blood sugar, other herbal teas offer invaluable indirect support for diabetes management by fostering overall well-being, reducing stress, and improving digestion. Peppermint and chamomile teas are perfect examples of these comforting, beneficial brews.
* Peppermint’s Digestive Relief: Peppermint tea is renowned for its refreshing flavor and its ability to soothe the digestive system. The active compound, menthol, has antispasmodic properties, meaning it can help relax the muscles of the gastrointestinal tract. This makes peppermint tea an excellent choice for easing indigestion, reducing bloating, alleviating gas, and calming an upset stomach. A comfortable digestive system is crucial for overall health; when you’re not experiencing digestive distress, your body can focus its energy on other vital processes, and you’re less likely to experience discomfort that can contribute to stress. Sipping a warm cup of peppermint tea after a meal can provide a gentle, natural way to support healthy digestion and promote general comfort.
* Chamomile for Relaxation: Chamomile tea is a classic choice for winding down and promoting relaxation, and its benefits for stress reduction are particularly pertinent to diabetes management. The herb contains an antioxidant called apigenin, which binds to specific receptors in the brain, helping to reduce anxiety and induce sleepiness. Chronic stress can significantly impact blood sugar levels by triggering the release of stress hormones like cortisol, which can elevate glucose. Furthermore, poor sleep quality, often a byproduct of stress, can impair insulin sensitivity. By helping you relax, reduce anxiety, and improve the quality of your sleep, chamomile tea provides a gentle yet powerful way to indirectly support better blood sugar control and foster overall mental and physical well-being.
* Anti-inflammatory Effects: Beyond their well-known digestive and calming properties, both peppermint and chamomile teas also contain a variety of beneficial compounds with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Peppermint, rich in flavonoids and phenolic acids, and chamomile, abundant in chamazulene and apigenin, contribute to reducing systemic inflammation throughout the body. While not as potent as some of the direct blood sugar regulators, this general anti-inflammatory support is invaluable for individuals with diabetes, as chronic low-grade inflammation is often a contributing factor to the progression of the condition and its complications. Enjoying these teas regularly can contribute to a robust internal environment, promoting overall health and resilience.
Incorporating these beneficial teas into your daily routine can be a simple yet effective way to support your diabetes management goals, alongside a balanced diet and regular exercise. Whether you opt for the metabolic boost of green tea, the blood pressure support of hibiscus, the soothing warmth of ginger, the insulin-mimicking power of cinnamon, or the comforting calm of peppermint and chamomile, each cup offers a unique contribution to your well-being. Remember, while these teas offer promising benefits, they are not a substitute for prescribed medication or medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian before making significant changes to your diet, especially if you have diabetes, to ensure these choices align with your individual health plan and to monitor your blood sugar levels as advised. Sip mindfully, enjoy the process, and empower your health journey one delicious cup at a time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is generally considered the best tea for individuals with diabetes, and why?
Green tea is frequently highlighted as one of the best teas for people with diabetes due to its rich content of powerful antioxidants, specifically epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). These compounds are scientifically studied for their potential to improve insulin sensitivity and help regulate blood sugar levels. Regular, unsweetened green tea consumption can therefore be a valuable part of a holistic diabetes management plan, supporting metabolic health.
Beyond green tea, which other herbal teas are beneficial for blood sugar management?
Several other herbal teas offer promising benefits for blood sugar control. Cinnamon tea is often recommended for its potential to lower fasting blood glucose and enhance insulin sensitivity. Hibiscus tea can help manage blood pressure, a common concern for individuals with diabetes, and may also play a role in glucose regulation. Additionally, ginger tea and chamomile tea possess anti-inflammatory properties that can support overall well-being and potentially mitigate diabetes-related complications.
How does drinking tea specifically benefit people managing type 2 diabetes?
Drinking unsweetened tea provides multiple advantages for individuals managing type 2 diabetes. Teas, particularly green tea, contain polyphenols that can enhance the body’s sensitivity to insulin, allowing cells to more effectively absorb glucose from the bloodstream. Furthermore, opting for plain tea provides a calorie-free, sugar-free beverage alternative, crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels and staying hydrated without contributing to glucose spikes. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties also contribute to reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, common factors in diabetes progression.
Are there any types of tea or tea additives that people with diabetes should avoid?
Yes, individuals with diabetes should strictly avoid sweetened teas, including many bottled iced teas, commercial tea lattes, and instant tea mixes, which are often loaded with added sugars, syrups, and artificial flavors. Even if brewing at home, adding sugar, honey, agave nectar, or large amounts of milk and cream can negate any health benefits and significantly spike blood sugar. It is best to stick to plain, unsweetened brewed teas and, if needed, use zero-calorie natural sweeteners sparingly or enjoy the tea’s inherent flavors.
How much tea is recommended daily for someone with diabetes, and does caffeine content matter?
For most individuals with diabetes, consuming 2-4 cups of unsweetened tea daily is generally considered safe and beneficial. However, moderation is important, especially with caffeinated varieties like black or green tea. While green tea’s caffeine content is typically lower than coffee, excessive intake can impact sleep, potentially elevate stress hormones, and might temporarily influence blood sugar levels in some sensitive individuals. It is always wise to consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to determine the appropriate tea intake based on individual health conditions and medications.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8900010/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7325515/
- https://diabetes.org/food-nutrition/eating-well/beverages/water-and-other-drinks
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes/expert-answers/diabetes-diet/faq-20058148
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/type-2-diabetes-sweeten-tea-naturally-201602269022
- Health effects of tea
- https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/managing/eat-well/what-to-drink.html


